
Soldering is an indispensable technique in the world of electronics, DIY projects, and various other industries. Whether you're a seasoned professional or a novice just starting to explore the world of soldering, understanding the fundamental differences between soldering stations and soldering irons is crucial. These tools serve as the backbone of soldering work, each with its unique features and applications. Soldering station vs. soldering Iron, we will delve into the distinctions between soldering stations and soldering irons..
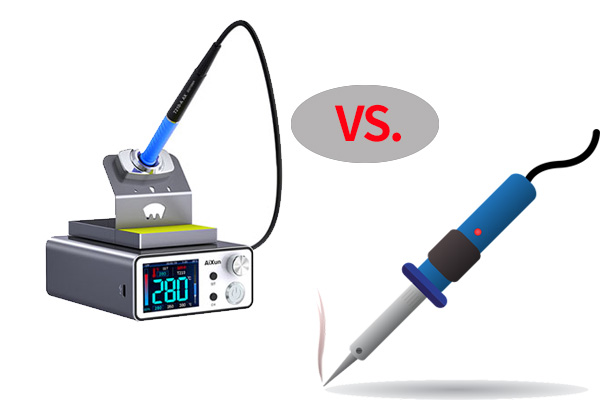

A soldering station is a sophisticated soldering tool that consists of two main components: a soldering iron and a control unit. This unique combination empowers soldering enthusiasts and professionals with precision, control, and versatility in their soldering tasks, making soldering stations an essential choice for various applications, especially in electronics and circuitry work.
Soldering Iron: At the heart of a soldering station is the soldering iron itself. This hand-held tool features a heating element and a soldering tip. The heating element rapidly heats up, while the soldering tip is responsible for melting the solder. Soldering iron tips come in different shapes and sizes, catering to various soldering needs.
Control Unit: The control unit serves as the brains behind the soldering station. It connects to the soldering iron via a cable and allows users to precisely control and adjust the iron's temperature. This temperature control is pivotal for soldering tasks that demand specific heat levels. The control unit often includes a digital or analog display for easy temperature settings.
Temperature Control: A standout feature of a soldering station is its precise temperature control capability. Users can set and maintain the desired soldering temperature throughout their work. This level of control is especially critical for delicate electronic components, ensuring that the right amount of heat is applied without the risk of damage.
Stability: Soldering stations are engineered for stability. They maintain a consistent temperature, mitigating temperature fluctuations that could affect soldering quality. This stability is vital for achieving reliable and consistent solder joints.
Safety Features: Many soldering stations incorporate safety features like auto-off timers and overheat protection. These safety mechanisms help prevent overheating, safeguarding the soldering iron and reducing the risk of fire hazards.
Versatility: Soldering stations are versatile tools, suitable for a wide range of soldering tasks. Whether you're soldering electronic components, wires, connectors, or other materials, the adjustable temperature settings and interchangeable tips of a soldering station make it adaptable to diverse soldering needs.
In summary, a soldering station comprises a soldering iron and a control unit, offering precision, stability, and safety in soldering tasks. This powerful tool is the go-to choice for those seeking accurate and controlled soldering results. With a clear understanding of what a soldering station entails, let's explore the characteristics of a regular soldering iron in the following sections.
In contrast to a soldering station, a regular soldering iron is a simpler soldering tool commonly used for various soldering tasks. It operates based on a straightforward design, making it accessible for beginners and suitable for less demanding soldering work.
A regular soldering iron consists of a few key components:
Heating Element: The core of a soldering iron is its heating element, often made of ceramic or nichrome wire. When the soldering iron is powered on, the heating element heats up rapidly, producing the necessary heat for soldering.
Soldering Tip: The heating element is attached to a soldering tip, which is typically made of copper or other heat-conductive materials. The soldering tip directly contacts the components and solder during the soldering process.
Unlike soldering stations with precise temperature control, regular soldering irons usually have wattage-based temperature control. The wattage (measured in watts) determines how quickly the iron heats up and how hot it gets. Higher wattage soldering irons heat up faster and can reach higher temperatures.
While regular soldering irons are versatile and suitable for many applications, they come with some limitations:
Fixed Tips: Regular soldering irons often have fixed tips that cannot be easily changed. This limits their adaptability to different soldering tasks and may require using separate soldering irons for various applications.
Temperature Fluctuations: Unlike soldering stations that maintain a stable temperature, regular soldering irons may experience temperature fluctuations during use. This variability can affect soldering quality and consistency, making them less ideal for precise electronic work.
Limited Temperature Control: Most regular soldering irons lack precise temperature control. Users cannot adjust the temperature to specific degrees, which may be necessary for certain soldering tasks that require careful heat management.
Safety Concerns: Regular soldering irons require constant vigilance. Users must unplug them when not in use to prevent overheating, and there are fewer built-in safety features compared to soldering stations.
A regular soldering iron operates on the principle of heating a fixed-tip with a heating element, controlled by wattage. While versatile and suitable for a wide range of soldering tasks, regular soldering irons may lack the precision and stability that soldering stations offer.
Understanding the characteristics of both tools is essential for choosing the right one for your specific soldering needs. Let's uncover the key differences between soldering station and soldering iron in the next.
Ready to start on your soldering journey? Explore AiXun website for more in-depth articles, soldering tools recommendations, and expert tips to enhance your soldering skills.
Link to Soldering station Vs. Soldering iron: the Differences and Use Cases
Browse more Soldering Stations
 WhatsApp
WhatsApp