
When it comes to soldering, achieving the right temperature is crucial for successful and reliable joints. The soldering iron tip plays a vital role in transferring heat to the components and solder, but understanding its temperature ratings is often overlooked. In this article, we will delve into the importance of soldering iron tip temperature ratings and provide valuable insights to help you make informed decisions while soldering.
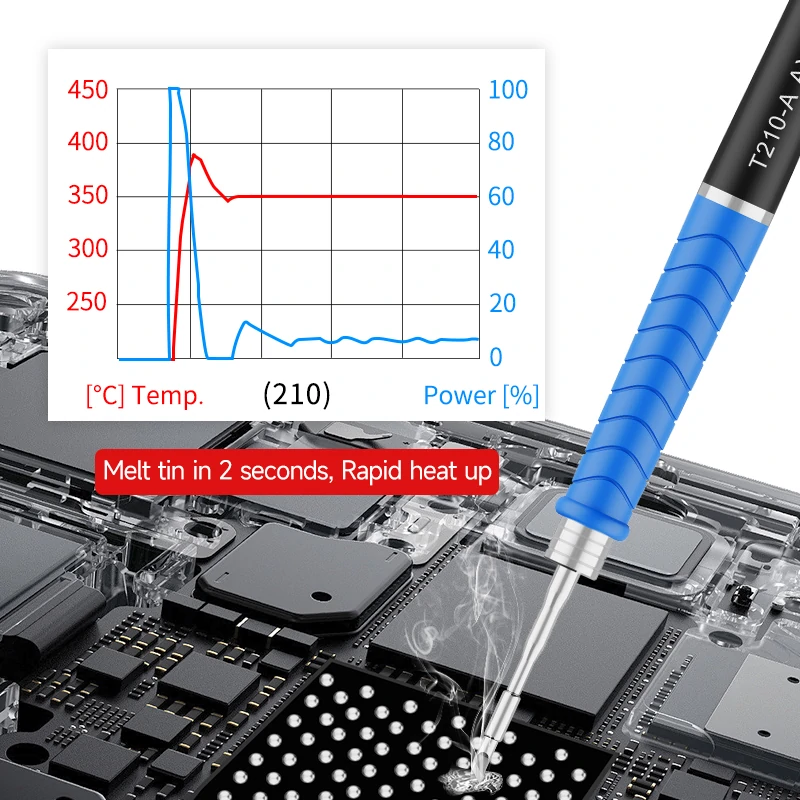
Soldering iron tips come with temperature ratings that indicate the optimal operating temperature range. The temperature rating is usually measured in degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F) and can typically range from around 300°C (572°F) to 450°C (842°F) or higher, depending on the tip and soldering iron model.
Selecting the appropriate temperature for your soldering iron tip depends on several factors, including the type of solder, the components you're working with, and the size of the joint. Different solders have different melting points, and various components are sensitive to heat. As a general rule, lower temperatures are suitable for delicate components and fine-pitched circuitry, while higher temperatures are required for larger components and thicker wires.
Soldering Iron Tip Material: The material composition of the tip influences its heat transfer capabilities. Tips made of copper are more efficient at heat transfer, while those with iron plating provide added durability. Each tip material may have different optimal temperature ranges.
Solder Type: Lead-based and lead-free solders have different melting points. It's crucial to use a temperature that allows the solder to melt and flow properly without overheating the components or causing damage.
Component Sensitivity: Certain electronic components, such as integrated circuits (ICs) and sensitive semiconductors, are highly susceptible to heat damage. Always refer to the manufacturer's guidelines or datasheets for temperature limits and recommendations. AiXun is the leading China manufacturer of intelligent electronics in areas like hardware, software, new materials, intelligent manufacture, and so on. If you have any questions, feel free to inquiry.
Joint Size and Complexity: Larger joints or those requiring a significant amount of heat transfer may require higher temperatures. Smaller, intricate joints necessitate lower temperatures to avoid overheating nearby components.
Use a Temperature-Controlled Soldering Iron: Investing in a soldering station with adjustable temperature settings provides precise control over the tip temperature. This allows you to tailor the temperature to the specific requirements of your soldering project.
Calibration and Verification: Periodically calibrate your soldering station or use a separate temperature verification tool to ensure the displayed temperature matches the actual tip temperature. This step helps maintain accuracy and consistency.
Experiment and Practice: It's essential to gain experience and familiarize yourself with different temperature settings by practicing on scrap components or prototype boards. This experimentation will help you understand the effects of temperature on different soldering scenarios.
Observe Solder Behavior: Pay attention to the behavior of the solder during the soldering process. If it refuses to melt or flows sluggishly, the temperature may be too low. On the other hand, if the solder rapidly evaporates or exhibits excessive splattering, the temperature may be too high.
Understanding soldering iron tip temperature ratings is crucial for achieving high-quality solder joints and avoiding component damage. Selecting the appropriate temperature setting requires considering factors such as solder type, component sensitivity, joint size, and tip material. By using a temperature-controlled soldering iron, calibrating the equipment, and gaining experience through practice, you can master temperature control and achieve reliable soldering results. Remember, precision and a keen understanding of temperature requirements are the keys to successful soldering projects.
 WhatsApp
WhatsApp